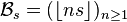无意看到的题目.. 因为是中文的就猫了一眼, 觉得挺水就做做, 结果一做就是一下午.. NOI还有点名堂
无意看到的题目.. 因为是中文的就猫了一眼, 觉得挺水就做做, 结果一做就是一下午.. NOI还有点名堂
开始觉得就是博弈+简单DP, 右图每一个格子 (a, b) , 玩家一次取石子以后能变成的状态是 (a-i, b) , (a, b-i) , 或者 (a-i, b-i) , 只要路线上存在lose, 赋值为win, 否则赋值lose. 整个表格是对称的. 自底向上DP就可以解决.
然后看了discuss, 存在O(1) 的算法..
Beatty sequence Wiki 讲解 , 看一下就了了..
The positive irrational number
generates the Beatty sequence
If
then
is also a positive irrational number. They naturally satisfy
and the sequences
and
form a pair of complementary Beatty sequences.
For r = the golden mean, we have s = r + 1. In this case, the sequence
, known as the lower Wythoff sequence, is
and the complementary sequence
, the upper Wythoff sequence, is
上下两个数列整好组成 lose 状态的坐标 (1,2) (3,5) (4,7) … 至于为什么等我有空会思考update一下 =D 好神奇阿
其中r是黄金分割律, 即 (1+sqrt(5))/2
则如果m在第一个数列里,则
m=[nr]=nr-x
m/r=n-x/r
其中x属于[0,1) , 先求出n再判断m/r是否在等式右边的区间里即可. 再返回n判断输入的b是否在二队列中相应的位置
Code:
[cpp]
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
//return num in Beatty sequence(r=golden mean), -1 if not belong to
int Br(int m) {
static const double P=(1+sqrt(5.0))/2;
double foo=m/P;
int n=(int)foo;
if(foo-n>0.999999)
n++;
n++;
if(foo>(n-1/P))
return n;
else
return -1;
}
int main() {
int a,b;
while(scanf("%d%d",&a,&b)!=EOF) {
if(a>b)
std::swap(a,b);
int foo=Br(a);
bool win=true;
if(foo!=-1)
if(a+foo==b)
win=false;
if(win)
printf("1\n");
else
printf("0\n");
}
return 0;
}
[/cpp]