这两道题用的理论都是一样的, 贪心算法很简单, 关键是怎么证明:
理论基础
首先需要了解的是..
序理论(中文) http://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-sg/%E5%BA%8F%E7%90%86%E8%AE%BA
偏序集(中文) http://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-sg/%E5%81%8F%E5%BA%8F%E5%85%B3%E7%B3%BB
Dilworth’s Theorem(wiki没中文) http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Dilworth’s_theorem
Dilworth的对偶定理的证明我看的lambda2fei牛这里写的, 英文太长实在是没法看..
Dilworth本身的证明我还没有看.. TODO. 但是lamb牛写的chain(链)和antichain(反链)的转换我一看就明了, 通过这种转换可以很容易的使用Dilworth定理, 同样也可以证明Dilworth定理, 我还没看原本怎么证明的..(稍后update) 这种方法已经很牛逼了感觉
为了文章完整性引用一下他的证明
Dilworth定理说的是:对于一个偏序集,其最少链划分数等于其最长反链的长度。
Dilworth定理的对偶定理说的是:对于一个偏序集,其最少反链划分数等于其最长链的长度。
Dilworth定理先不证,有空再不上来,其对偶定理证明如下:设一个偏序集S的最少反链划分数是p,最长链长度是r。
1.先证p≥r。这是显然的,因为最长链长度是r,r个元素中的任意两个都可以比较,因此它们必定两两属于不同的反链,因此反链个数≥r,即p≥r。
2.再证r≥p。设X1=S。找出X1的所有极小元组成集合Z1,将其从X1删之,得到X2,再找出X2的所有极小元组成集合Z2(特别注意Z2中的任何元素a2,在X1中必然存在一个元素a1使得a1≤a2,否则a2可以放到X1中,这与X1的选取矛盾),再将Z2从X2中删除,得到X3,……这样一直下去,总存在一个k使得XK不空但X(K+1)为空。这样便得到一条链a1,a2,a3,……,ak,其中ai属于Xi。由于r是最长链长度,因此r≥k。另一方面,我们也得到了一个反链划分,即X1,X2,X3,……,XK。由于p是最少反链划分,因此k≥p。因此有r≥p。证毕。
1065详解
要求的就是集合的chain的划分最小数目.
对于题目中给出的关系P={l <= l’ and w <= w’}, 我们定义关系P’={l < l’ and w > w’} (并不是l<=l’), 那么对于原来关于 P 可比较的两个元素, 关于 P’ 则不能比较, 原来不能比较关于 P’ 就可比较. 相应的 P 的 chain/antichain 就成为 P’ 的 antichain/chain .
这样定义后, 就可以放下原题, 题目变成找一堆元素中的最少antichain数目, 根据Dilworth定理对偶定理的证明过程(如上), 每次剥离出 Xi 中的所有极小元, 直到 Xi 为空, 剥离的次数就是答案 .
剥离的次数 == k== 关于 P’ 的最长chain的长度(对偶定理) == 关于P的最长antichain的长度(chain转换) == 关于P的chain的最少划分数(Dilworth)
有点绕.. 但比看上去简单
实例:
考虑元素集 (1,2) (2,3) (2,4) (3,1) (3,2) (3,3) (3,5) (4,1) (5,2) (6,1) (6,7) (7,1)
每次取出关于 P’ 的极小元, 过程如下
[cpp]
(1,2) (2,3) (2,4) (3,1) (3,2) (3,3) (3,5) (4,1) (5,2) (6,1) (6,7) (7,1)
(3,1) (3,2) (3,3) (4,1) (5,2) (6,1) (7,1)
(4,1) (5,2) (6,1) (7,1)
(6,1) (7,1)
[/cpp]
因为P’是严格的偏序关系, 每次取出的最小元 x 就要满足找不到 y 使 y P’ x (如果是不严格的偏序就要考虑自反的情况)
怎样取极小元呢, P’ 的极小元是 “在 l 比它小的元素中, 找不到 w 比它大的元素”, 按照代码中的 comp() 排序以后(先l后w), 以这个条件找极小元的集合, 等价于从第一个元素开始找, 后一个元素的w’>=前一个元素的w, 的元素集合. 比如(1,2) (2,3) (2,4) (3,5) (6,7), 满足2<=3<=4<=5<=7, 这样贪心就很简单了
3636详解
和1065基本一样, 有了上面的理论就很好做了. 关键在于 P => P’ 的转换
P={w1<w2 && h1<h2} (大于小于无所谓)
所以 P的”可比较”关系 Pc = {w<w2 && h1<h2 || w1>w2 && h1>h2}
所以 P’c= {w1<w2 && w1>=h2 || w1>w2 && h1<=h2 || w1==w2}
所以 P’= {w1<=w2 && h1>=h2}
这里 P’ 是具有自反性和反对称性的非严格偏序关系.
这里就有一个问题: 集合内元素具有互异性, 但是题目中的元素有可能存在两两相同的, 怎么办?
我们可以想像我们上面讨论的集合是题目中的元素”只保留相同元素中的一个”后的集合, 这个集合中的元素a包含了n个题目中的相同元素, 就有两种处理的方法:
方法一: 把这n个元素看作一个a来”剥离”(取最小元), 1065就是这样, (1,2)(1,2)(1,2)在一起剥离是可以的, 因为1<=1,2<=2, 符合P的比较条件
方法二: 剥离a后a还存在于后来的Xi中, 并且n-=1, 直到n==0 a消失, 3636就要这么干, (1,2)(1,2)是不能放在一起的, 不符题意(P), 可以证明这样干是最优的(如果不取这个最小元, 这次执行后得到的Xi要比取的元素多一个, 不取白不取)
经过思考, 这道题最终要做的贪心是: 先按照w排序, w的互异值从小到大为w1,w2..wk, 然后在w==w1的元素里找到h最大的元素取出, 再在w2中找h最大的元素取出, 并且这些h需要满足条件:比前一个取出的元素的h大, 取完一次result++, 直到取空
代码点下面:
Continue reading

 generates the Beatty sequence
generates the Beatty sequence
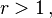 then
then  is also a positive irrational number. They naturally satisfy
is also a positive irrational number. They naturally satisfy
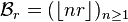 and
and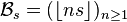
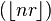 , known as the lower Wythoff sequence, is
, known as the lower Wythoff sequence, is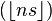 , the upper Wythoff sequence, is
, the upper Wythoff sequence, is